Sequences and Series - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
CH-09 Sequences and Series
the ratio of first to the last of n A.m.’s between 5 and 35 is 1 : 4. The value of n is
9
11
10
19
All the terms in A.P., whose first term is a and common difference d are squared. A different series is thus formed. This series is a
H.P.
G.P.
A.P.
none of these
If A, G, H denote respectively the A.M., G.M. and H.M. between two unequal positive numbers, then
A = GH
The next term of the sequence 1, 1, 2, 4, 7, 13,…. Is
21
24
none of these
19
The sum of all non-reducible fractions with the denominator 3 lying between the numbers 5 and 8 is
31
52
41
39
- Fill in the blanks:
The general term or nth term of G.P. is given by an = ________. - Fill in the blanks:
The third term of a G.P. is 4, the product of the first five terms is ________. Find the sum of first n terms and the sum of first 5 terms of the geometric series
Find the 12th term of a G.P. whose 8th term is 192 and the common ratio is 2.
Find the sum of 20 terms of an AP, whose first term is 3 and last term is 57.
Find the sum to n terms of the sequence: log a, log ar, log ar2, ...
The nth term of an AP is 4n + 1. Write down the first four terms and the 18th term of an AP.
Find the sum to n terms in each of the series
Find the sum to n terms in each of the series 52 + 62 + 72 + ..... + 202
If a and b are the roots x2 - 3x + p = 0 and c, d are roots of x2 - 12x + q = 0 where a, b, c, d form a G.P. Prove that (q + p):(q - p) = 17:15.
CBSE Test Paper 01
CH-09 Sequences and Series
Solution
- (a) 9
Explanation:the sequence is
here a=5 and b=35
we know that,
According to question, - (d) none of these
Explanation: the series obtained will not follow rules of AP, GP and HP - (d)
Explanation:
Given the numbers are a and b, then we have
and
Now - (b) 24
Explanation:
The given sequence can be expressed as
, - (d) 39
Explanation:
We have
Hence the fractions between5 and 8 with 3 as denominator will be and in this only and are reducible
Now and is an A.P with first term a = and
Hence Sum =
Hence the sum of non redubile fractions = 52-(6+7)=52-13 = 39 arn-1
45
a = 1, r =
Let a be the first term of given G.P. Here r =2 and a8 = 192
an = arn-1
a12 = ar12 - 1
= 3 1024 = 3072We have, a = 3, l = 57 and n = 20
Sn = [a + l]
S20 = [3 + 57]
= 10 60
= 600We have sequence log a, log ar, log ar2, ...
Above sequence can be expressed as log a, (log a + log r), (log a + 2 log r), ...
[ log mn = log m + log n and log nr = r log n]
which is clearly an AP with, a = log a and d = log r
We know that, sum of n terms,
Sn = [2a + (n - 1)d]
Sn = [2 log a + (n - 1) log r]
= [log a2 + log rn-1] [x log a = log ax]
= [log a2rn-1] [ log a + log b = log ab]Here, Tn = 4n + 1 ...(i)
On putting n = 1, 2, 3, 4 in Eq. (i), we get
T1 = 4(1) + 1 = 4 + 1 = 5
T2 = 4 (2) + 1 = 8 + 1 = 9
T3 = 4 (3) + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13
and T4 = 4 (4) + 1 = 16 + 1 = 17
On putting n = 18 in Eq. (i), we get
T18 = 4(18) + 1 = 72 + 1 = 73
Hence, the first four terms of an AP are 5, 9, 13, 17 and 18th term is 73.Given: to n terms
Let [By partial fraction]
Then 1=A(n+1) + Bn
Put n=0 then A=1
Put n=-1 then B=-1
.........
And Sn = a1 + a2 + a3 + ........ + an
Given: 52 + 62 + 72 + ....... + 202
= (12 + 22 + 32 + ...... + 202) - (12 + 22 + 32 + 42)
Let
b = ak And
c = bk = (ak)k = ak2
Also
d = ck = (ak2)k = ak3
a
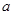 and b
and b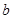 are the roots x2 - 3x + p = 0
are the roots x2 - 3x + p = 0 a + ak = 3
a(1 + k) = 3 ……….(i)
And
a(ak) = p
a2k = p ......(ii)
Also c, d are roots of x2 - 12x + q = 0
ak2 + ak3 = 12
ak2(1 + k) = 12 ……….(iii)
And
ak2(ak3) = q
a2k5 = q ……….(iv)
Dividing eq. (iii) by eq. (i),
k2 = 4
Now
Therefore, (q + p):(q - p) = 17:15