Excretory Products - Test Papers
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
CLASS - XI BIOLOGY
(Excretory Products and their elimination)
General Instruction:
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question No. 1 to 3 carry one marks each. Question No. 4 to 6 carry two marks each. Question No. 7 and 8 carry three marks each. Question No. 9 carry five marks.
1. In which part of nephron filtration takes place?
2. What difference is observed in the ascending and descending limb of Henle’s loop witch reference to permeability of water?
3. What is the PH of urine.
4. Differentiate between Rennin and Renin?
5. What are the two intrinsic mechanisms that provide auto regulation of glomerular filtrate? Explain any one of these.
6. How is the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting tubule controlled for regulating the water content inside the body?
7. Person suffering from very low blood pressure pass no urine why? What suggestion would you offer for the removal of waste products from the blood in such a situation.
8. Explain briefly how micturation is a reflex process; but is also under some voluntary control.
9. Describe briefly the structure and function of renal corpuscle.
CBSE TEST PAPER-1
CLASS - XI BIOLOGY (Excretory Products and their elimination)
[ANSWERS]
Ans 01. Glomerulus.
Ans 02. Ascending limp of Henle’s loop is impermeable to water. Descending limb of Henle’s loop is permeable to water.
Ans 03. It is slightly acidic, PH – 6.0
Ans 04.
| Rennin | Renin |
1. | Secreted from the peptic cell or gastric glands in stomach. | Secreted from the juxtaglomerular cells of afferent renal artery in the renal cortex of kidney. |
2. | The rennin is proteolysis enzyme. | Renin is a hormone but it acts as enzyme also. |
3. | Helpful in the digestion of milk of protein. | Converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin – II |
4. | Released in inactive form. | Released in active form. |
Ans 05. Two intrinsic mechanisms that provide autoregulation, Myogenic mechanism and Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) JGA – A special cellular apparatus is located in kidney where DCT passes close to Bowman’s capsule between afferent and efferent arterioles. The JGA cells secrete rennin that modulate blood pressure there by regulating renal flow and GFR.
Ans 06. 1) When the water content inside the body is low, the osmorecepters stimulates theadenohypophysis to releases vasopressin / ADH.
2) Vasopressin / ADH render the DCT and collecting tubule permeable to water. So, water is reabsorbed.
3) When the water content in the body is normal, there is no release of ADH.
4) The tubule is impermeable to water and water is eliminated in the urine.
Ans 07. It is because, the blood to pass through the glomerulus of the nephron must have required amount of pressure in it. If the pressure is not sufficient it will not flow through glomerulus and filtration would not the take place, hence no urine would be formed. This is quite harmful to the person as waste products go on accumulating in the body.
To avoid this, a person should be advised take sufficient amount of water and medicine to keep the blood pressure at optimum level.
Ans 08. 1) Micturation is act of voiding urine
2) It accomplished by the simultaneous contraction of the smooth muscles of urinary bladder wall and the relaxation of the skeletal muscle sphincters around the opening of the bladder.
3) As the bladder wall becomes stretched due to accumulation of urine, the stretch receptors in the wall of the bladder generate nerve impulse that are carried to sense neurons to the spinal cord and brain produce the sensation of fullness.
4) But the sphincter muscles can also be relaxed voluntarily and there by the smooth muscles of the bladder are allowed to contract under autonomic control and the content of the bladder can be emptied.
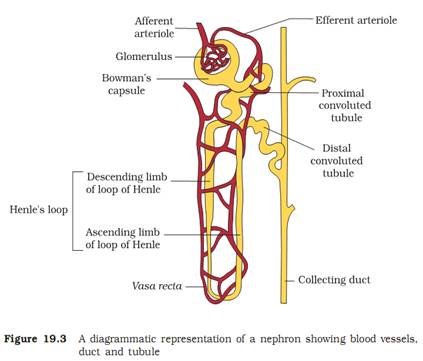
Ans 09. Renal Corpuscle – It is the main excretory organ in the kidney. Nephrons are the functional units of kidney of renal corpuscle. There are about 102 million nephrons in each kidney in man.
Structure of nephron – The nephron is a thin, long, twisted tubular structure. The tubule of each nephron starts as a up – shaped called Bowman’s capsule. There is a globular tuft of capillaries in the hollow of the cup. The Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus together form a globular body called the renal corpuscle. Blood enters the glomerular capillaries through an afferent arteriole and leaves the glomerulus through as efferent arteriole.
Urine is formed by the filtration of a protein free fluid from the glomerulus into lumen of the Bowman’s capsule.
There are 3 parts of a nephron –
(i) proximal nephron (ii) hoop of Henle and (iii) distal nephron.
A long highly coiled and tubule trusted starts form the neck of the Bowman’s capsule. It is called the PCT (Proximal Convoluted tubule). It continues into a thin–walled straight tubule, then loops like segment of the tubule is called the Henle’s loop. It has thin descending limb and thick ascending limb. The Henle’s loop continuous into another segment of coiled and twisted tubule called DCT (Distal convoluted tubule). The terminal part of DCT is a straight short tubule called the collecting duct. The collecting duct runs down to the medulla again conducting the collected urine towards the medulla.
The collecting ducts unite with each other in the medulla to form the larger ducts called Ducts of Bellini. These ducts rue through the renal pyramids and open into renal pelvis.
The efferent arteriole gives a capillary network around the tubule in the cortex. It also fives rise to some parallel wise, thin walled straight capillaries called vasa rectae. They help to maintain reabsorbed ions and urea in the intestinal fluid and maintain osmotic pressure in the kidney.
Functions – Various part of nephron perform deferent function but the main function is liberation of metabolic waste from the body and maintain osmotic pressure of fluid in the body.